Choosing the Right Material for Laser Processing Projects
Posted on August 19, 2025 in Blogs

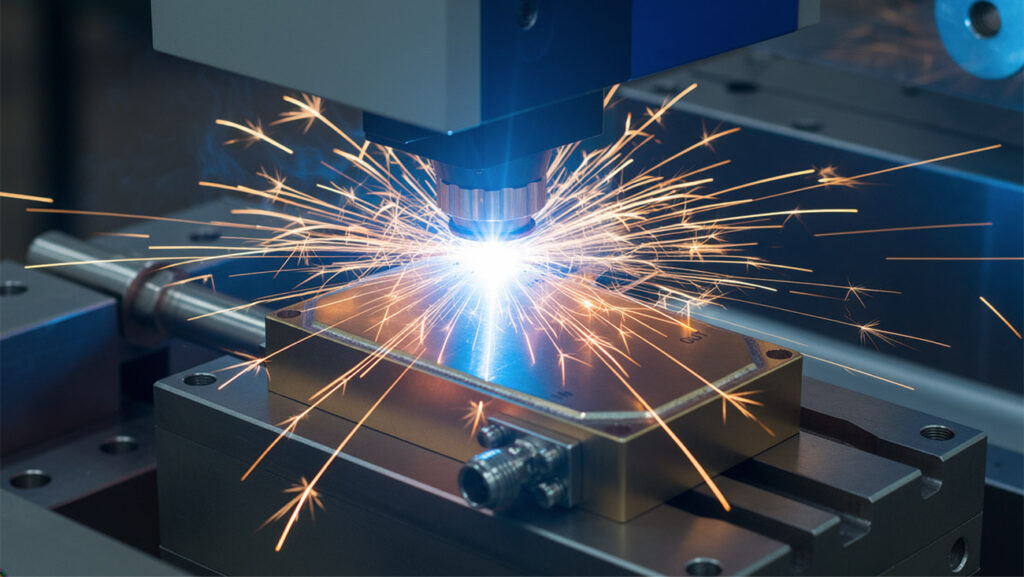
Selecting the right material is one of the most critical decisions in any laser processing project. The choice directly impacts precision, efficiency, and overall product performance. Whether you’re developing a medical device, aerospace component, or advanced electronics part, understanding how materials interact with laser technology can help you achieve the best possible results.
Why Material Selection Matters
Laser processing relies on the absorption of focused light energy to cut, weld, mark, or ablate material. Different substrates respond uniquely to laser energy based on their reflectivity, thermal conductivity, and melting point. Choosing the wrong material—or an incompatible grade or thickness—can result in poor edge quality, excessive heat damage, or structural weaknesses.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Materials
- Material Type: Metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites each have specific properties that affect laser performance. For example, metals like stainless steel and titanium are ideal for laser welding due to their strength and heat resistance.
- Thickness: Material thickness influences how much power is required and whether the cut or weld can be achieved cleanly.
- Reflectivity: Highly reflective materials (such as copper and aluminum) may require specialized laser sources to ensure efficient energy absorption.
- Thermal Conductivity: Materials that dissipate heat quickly need controlled energy input to avoid incomplete cuts or weak welds.
- Surface Finish: Coatings, surface roughness, and pre-existing contamination can impact laser precision and quality.
Common Materials Used in Laser Processing
- Metals: Stainless steel, titanium, Nitinol, Inconel, and aluminum are widely used in medical, aerospace, and electronics applications.
- Ceramics: Alumina, sapphire, and other advanced ceramics are ideal for microelectronics and optical applications due to their heat resistance and durability.
- Polymers: Certain plastics can be precisely cut or welded with lasers, though care must be taken to avoid melting or toxic fumes.
- Composites: Used in aerospace and automotive components, they require controlled laser parameters for clean processing.
Best Practices for Material-Laser Compatibility
- Prototype First: Early testing helps optimize power levels, speed, and focus for each material type.
- Use Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Guidelines: Following best practices for part geometry and joint design reduces rework and material waste.
- Partner with Experts: Collaborating with an experienced laser processing provider ensures you select materials that balance cost, performance, and manufacturability.
How Accumet Helps Optimize Material Selection
At Accumet, we specialize in guiding clients through the entire laser processing workflow—from material selection to final part delivery. With decades of experience across metals, ceramics, and specialty materials, we help manufacturers make informed decisions that ensure success in precision applications.
Contact Accumet today to discuss your project and get expert advice on the best materials for your laser processing needs.